physiologic tooth mobility
It should fulfill esthetic appearance and should be comfortable for the patient. Tooth mobility is the term used to describe loose teeth in the jaws or the alveolar bone.
Tooth Mobility And Periodontal Therapy My Dentist Toluca Lake
Not irritate soft tissues.

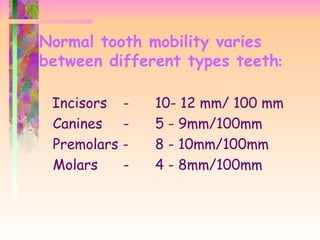
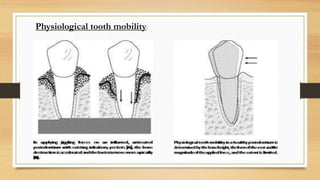
. This mobility is termed as physiologic mobility. Gum Disease and periodontal disease. Tooth mobility of about 025 mm is present normally in all the individuals and is considered healthy.
Measurement of tooth and implant mobility under physiological loading conditions. 1077339 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms Dental Stress Analysis Facial Musclesphysiology Humans Mastication Periodontiumphysiology Toothphysiology Tooth Mobility. Allow adequate oral hygiene.
This mobility is termed as physiologic mobilityThe reason for this mobility is that the tooth is not fused to the alveolar bone directly but is attached to the sockets by the periodontal ligament. Physiologic tooth mobility it refers to moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue muhleman1951 korber1971 lindhe 1989 normal tooth mobility varies between different types teeth. Article in French Daniel A Aouizerat C Fournier B Brulin H Rassat P Praud J.
Stabilize the injured toothteeth in its correct position and maintain adequate stabilization throughout the splinting period. Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. Pathologic tooth mobility 1.
Maintenance of adequate oral hygiene should be possible. Occlusal movements should not be interfered. Fixed reference point should be selected eg adjacent tooth that is not mobile and pressure should be applied in horizontal buccal-oral direction to the tooth we are testing.
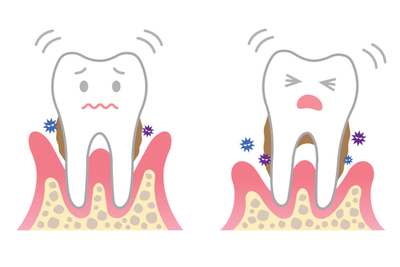
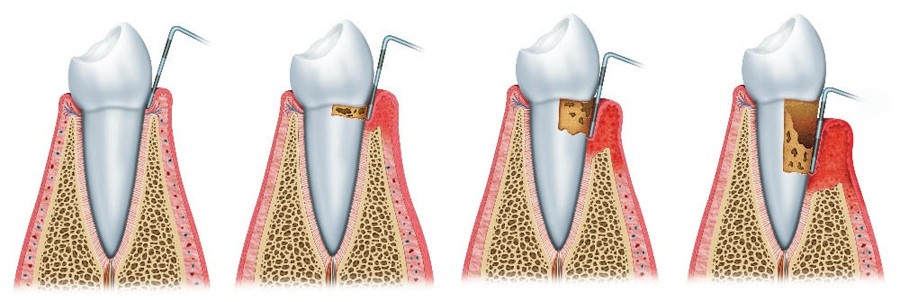
This video is about How to assess TOOTH MOBILITYPdf notes available. Tooth mobility is a clinical sign that may reflect the degree of periodontal destruction caused by localised infections in the gums and the structures surrounding the teeth ligaments and alveolar bone and providing support and stability. These infections are produced by bacteria originating in bacterial plaque.
Tooth mobility should be determined using two single-ended instruments eg mouth mirror and probe. The common causes in tooth mobility as follows. Therefore determining tooth mobility gives useful information for the diagnosis and evaluation of the treatment outcome.
It refers to a moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue. Request PDF Measurement of tooth and implant mobility under physiological loading conditions. Physiological tooth mobility seen in healthy teeth depends on the biophysical characteristics of the periodontal tissue whereas pathological tooth mobility is the result of the loss of periodontal support.
Grade 0 mobility Normal physiologic tooth mobility. Physiologic mobility represents the range of mobility level considered. Allow physiologic tooth mobility to aid in periodontal ligament healing.
Parafunctional habits like bruxism clenching or grinding of teeth. Tooth mobility of about 025 mm is present normally in all the individuals and is considered healthy. Download link is as follows.
In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. Tooth mobility data on a scale of 03 were related to changes in attachment levels for three grades of. Nevertheless the highest physiologic peaks of passive bone stimulation through compression.
Allow pulp sensibility testing and endodontic access. Tooth mobility is the term used to describe loose teeth in the jaws or the alveolar bone. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years.
Pathologic process of jaws. Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Rev Belge Med Dent. Mobility beyond the physiologic range is termed.
Physiologic dental mobility. Traumatic injuries to dento alveolar unit. It should be nonirritating to soft tissues.
It should allow physiologic tooth mobility. It should allow pulp sensibility testing and endodontic access. Not interfere with occlusal movements.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. Article in Dutch Author D vanSteenberghe. Generally speaking there is a small amount of physiological.

Body Cavities And Membranes Medical School Studying Nursing School Medical Anatomy

Effects Of Periodontitis Associated Tooth Mobility With Positive Feedback Download Scientific Diagram

Cmtautodom Gif 397 435 Pixels Teeth Diseases Neurology Cmt

Pdf Teeth Mobility Measurement A Laser Vibrometry Approach

Biomechanical Analysis For Total Mesialization Of The Mandibular Dentition A Finite Element Study Kawamura 2019 Orthodontics Craniofacial Research Wiley Online Library

Guide To Proper Tongue Posture Mewing The Great Work Tongue Thrust Mew Postures

A Schematic Presenting The Measurement Of Pd Between The Tooth And Download Scientific Diagram

Pin By Jennifer York On Cmt Charcot Marie Tooth Teeth Diseases Point Mutation Cmt

Image From Http Www Mhhe Com Biosci Esp 2001 Saladin Folder Structure Su M3 S1 Assets Images Sum3s1 1 Jp Joints Anatomy Synovial Joint Anatomy And Physiology
Tooth Mobility And Periodontal Therapy My Dentist Toluca Lake

Orthodontic Tooth Movement The Biology And Clinical Implications Li 2018 The Kaohsiung Journal Of Medical Sciences Wiley Online Library

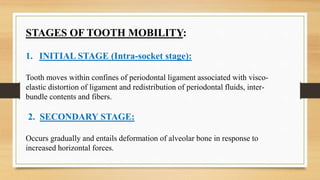




0 Response to "physiologic tooth mobility"
Post a Comment